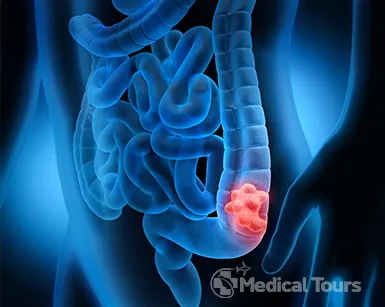
What Is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer is also known as bowel cancer or colorectal cancer is the cancer of the large intestine. It starts from the lower end of the large intestine commonly known as the rectum. After beginning from the rectum, it moves to other parts of the colon. It begins as non-cancerous polyps in the early stages. Polyps are non-cancerous small lumps of cells on the colon's inner surface. Screening can be used to detect non-cancerous polyps. Colon cancer is more likely to develop after the age of 50. Therefore, after the age of 50, it is strongly advised to have regular screenings.
Stages of Colon Cancer
Stage 1
In the first or early stage of cancer, it is indicated that the cancer is confined inside the colon. In the beginning, the cancerous cells grown into the layers of the colon are known as mucosa and submucosa.
Stage 2
In the second stage cells began to move out of the colon and start migrating to other areas within the colon. It is further subdivided into 2A, 2B, and 2C based on the extent to which the cancerous cells have spread. Cells in stage 2A usually reach the outer layers of the colon, whereas cancerous cells in stage 2B spread past the outer layer of the colon to membranes that hold the abdominal organs. Cancer may have spread to nearby organs or structures in stage 2C.
Stage 3
In the third stage that is before reaching the final stage, the cancerous cell spreads to nearby lymph nodes. It is further subdivided into 3A, 3B, and 3C based on the number of lymph nodes affected by cancer. The lymph node near the colon is affected in stage 3A. If two to three lymph nodes are affected, the diagnosis is 3B; if four or more lymph nodes are affected, the diagnosis is 3C.
Stage 4
In the fourth and final stage the cancerous cells start to spread to other parts of the body. When a patient reaches this stage, the cells start to spread to nearby organs such as the liver or lungs. When a nearby organ is affected, the stage is 4A, and when cancerous cells have spread to one or more distant organs, the stage is 4B.
Types of Colon Cancer
Hereditary colorectal cancer
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer arises in several variations, the most prevalent of which is adenocarcinoma. Carcinoid tumors, gastrointestinal stromal tumors, and colorectal lymphoma are some of the other forms.
Hereditary colorectal cancer
Hereditary colorectal cancers, such as hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) and familial adenomatous polyposis, are hereditary colorectal cancers in which several generations of a family have developed colorectal cancer (FAP).
Adenocarcinomas
Tumors that begin in the lining of internal organs are known as adenocarcinomas. The term "adeno" refers to a gland. These cancers begin in glandular cells or cells that secrete something. They can develop in a variety of organs, including the lung and the breast. Early tumors in colorectal cancer begin as tiny adenomatous polyps that expand and eventually become malignant tumors. Adenocarcinomas make up the vast majority of colorectal cancers.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
Tumors that originate in the muscular tissue of the digestive tract, however, rarely develop in the colon, are known as Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST). They may appear benign (noncancerous) at first, but many of them eventually develop into cancer. Sarcomas are what happens when this happens. If the tumor has not spread, surgery is the most common treatment.
Lymphoma Cancer
A lymphoma is cancer that typically starts in a lymph node, which is part of the immune system. However, it can also start in the colon or rectum.
Carcinoids
Carcinoids are tumors that start in special hormone-producing cells in the intestine. Often, they cause no symptoms. Surgery is the usual treatment
Turcot Syndrome
Turcot syndrome is a rare disorder that includes colorectal polyposis, colon cancer, and brain tumors. Mutations in different genes have been found in individuals with this syndrome, including mutations in the APC, MLH1, and MSH2 genes. For this reason, Turcot syndrome is said to be genetically heterogeneous.
Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by the following symptoms:
Macules of Melanocytic (dark blue or brown moles) these moles can be found on the lips, around the eyes, nose, and anus, as well as around and/or in the mouth. Dark moles on the fingers are also possible. By adulthood, the lesions may have faded. Multiple polyps in the stomach and intestines.
Increased risk of benign (noncancerous) ovarian and testicular cancers. Cancers of the stomach, esophagus, breast, colon, and pancreas are all at a higher risk.
Mutations in the STK11 gene on chromosome 19, which operates as a tumour suppressor gene, cause Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
The symptoms of colon cancer vary from person to person, but here are some of the more common ones.
- Weakness
- Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding
- Sudden weight loss for no apparent reason
- The sensation of being full in the abdomen
- Constant abdominal discomfort, as well as stomach pain, gas, and cramps
- Changes in bowel habits such as diarrhoea or constipation, as well as changes in stool consistency
If any of these symptoms remain persistent for a long period, one should visit a doctor and undergo screening as per the advice of the doctor. In the early stage of cancer, a person may not experience any symptoms as well. It is recommended to undergo screening after the age of 50. But doctors may recommend screening before the age of 50 to consider other risk factors.
Causes of Colon Cancer
- Age: People over the age of 50 are more likely to develop colon cancer. To detect it at an early stage, regular screening after the age of 50 is required. Despite the fact that rates of colon cancer in people under the age of 50 are rising.
- Family history of colon cancer: If you have a direct blood relation with a family history of colon cancer, it is recommended that you undergo colon cancer screening after the age of 50, or before the age of 50 if you have any symptoms.
- A high-fat, low-fibre diet: Diet is also linked to colon cancer. Diets high in fat, such as red meat, processed meat, and low in fibre, increase the risk of colon cancer. As a result, eating a well-balanced diet is advised.
Diagnosis of Colon Cancer
Colonoscopy: A diagnostic procedure that allows the doctor to examine the entire length of the large intestine.
Digital rectal exam: A digital rectal exam (DRE) is an exam of the rectum.
Faecal occult blood test (FOBT): A faecal occult blood test (FOBT) is a test to check stool (solid waste) for blood that can only be seen with a microscope.
Biopsy: A procedure in which tissue samples are removed from the body by a needle or during surgery for examination under a microscope to determine if cancer or other abnormal cells are present. There are many different types of biopsies.
Sigmoidoscopy: A diagnostic procedure that allows the doctor to examine the lower one-third of the large intestine.
Blood Count: This is a test to check for anemia (a result of bleeding from a tumor).
Barium enema (lower gastrointestinal series): A procedure that examines the rectum, the large intestine, and the lower part of the small intestine using a contrast dye containing barium.
Imaging Tests: Tests such as a CT (Computerised Tomography) scan, ultrasound, or MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) of the abdomen may be done to look for tumors or other problems. These tests may also be done if colorectal cancer has already been diagnosed to help determine the extent (stage) of the cancer.
Treatment Options of Colon Cancer
Small polyps are usually removed during the colonoscopy without the need for any incisions. Larger or more complex polyps are typically removed at Stanford using minimally invasive surgery that involves removing the segment of colon containing the polyp or polyps.
If cancer is discovered in the polyp, the more comprehensive approach may eliminate the need for a subsequent operation. If a cancer is discovered during a colonoscopy, the same operation is performed. Find out more about colonoscopies.
If cancer has not spread, surgery to remove the cancerous portion of the colon is often curative, with no further treatment required. Stanford specializes in multidisciplinary surgical treatment for colon cancer that has spread to other organs for locally advanced tumours or tumours that have spread to other organs. For locally advanced tumors or tumors that have spread to other organs, Stanford specializes in multidisciplinary surgical treatment for colon cancer that may involve urologists, liver surgeons, gynecologic oncologists, and reconstructive plastic surgeons, as necessary. They are experts in surgical removal and reconstruction strategies to give patients as comfortable a lifestyle as possible.
Colon Cancer Treatment Cost in India
Colon cancer is a common type of cancer that develops from the colon, which is a part of your digestive system. Colon cancer can be cured if detected in early stages, but not everyone has access to advanced medical facilities. The colon cancer treatment cost in India starts from $1100 (₹85460) to $9000 (₹699223). The variation in the cost is due to different treatment options and the intensity of the treatment.
Treatments performed include
A number of sessions and cycles
Cancer Stage
This factor has a significant impact on treatment costs. Treatment is determined based on the stage. The cost will rise in line with the complexity of the cancer.
Treatments performed include
The actual cost will be determined by the patient's and oncologist's treatment options. The costs of various treatments vary. The greater the number of treatments received, the higher the cost.
Place of Treatment
The cost of colon cancer therapy varies from hospital to hospital and city to city. A city with a high standard of living will naturally be more expensive than others. The cost of treatment in private hospitals will be higher than in government hospitals.
A number of sessions and cycles
Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are all delivered in cycles. Radiation therapy is administered in sessions. The cost is estimated based on the number of cycles and sessions. As a result, the more sessions, and cycles one undergoes, the higher the colon cancer treatment cost in India.
Medicines used in treatment
Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are all delivered in cycles. Radiation therapy is administered in sessions. The cost is estimated based on the number of cycles and sessions. As a result, the more sessions, and cycles one undergoes, the higher the colon cancer treatment cost in India.
Medicines used in treatment
Cancer treatment medications are extremely expensive. As a result, the type of medicine used in colon cancer treatment affects the treatment cost.
FAQs
If you are above 50, go through regular screening to get an idea about colon health.Add more fibres to your diet. Eat more vegetables and fruits. Have a balanced diet and put some cut on red meat.
If you are overweight, reduce your weight through regular exercise and other physical activities. Avoid smoking and reduce alcohol consumption.
Stools may look black or look like tar. If the stool colour is black, then it is a warning sign that blood from the colon might have made the stool dark red or black.
Poop colour may be bright red as well, in case of colon cancer. Irregular thin stool may also be colon cancer.
Depending on the type of surgery chosen by the doctor, most patients will spend no more than 5 days in the hospital. After the surgery, patients should be able to return to their normal routine in 2 to 4 weeks. Patients may experience fatigue, which will subside over time.